|
Código |
Descripción |
|
2910000 |
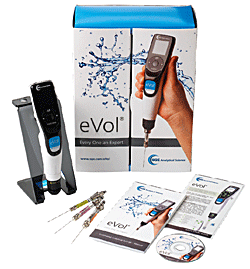
eVol® Kit.
Incluye eVol®, Alimentador Universal, Soporte Estándar y 3 jeringas eVol®
XCHANGE® (5, 50 y 500μL) |
|
2910100
|
eVol® Kit NMR.
Incluye eVol®, Alimentador Universal, Soporte Estándar y 3 jeringas eVol®
XCHANGE® (5μL con aguja de 11.5cm, 50μL con aguja de 11.5cm y 18cm y 500μL
con aguja de 11.5cm y 18cm). |
|
2910200 |
eVol® XR. Incluye eVol® XR, Alimentador Universal, Soporte Estándar y 3 jeringas eVol®
XCHANGE® (5μL, 100μL y 1000μL con aguja de 50mm). |
|
2910005 |
Motor eVol® sin jeringa
electrónica XCHANGE®. Requiere una Jeringa eVOL® XCHANGE® |
|
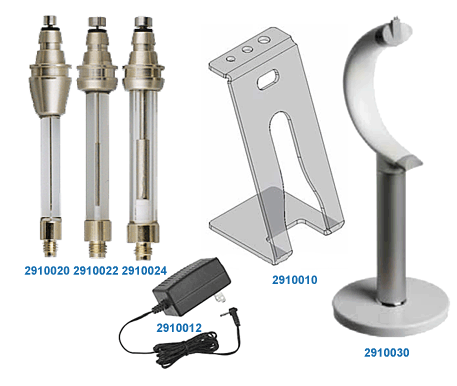
2910010 |
Soporte eVol® Estándar |
|
2910012 |
Cargador Universal |
|
2910020 |
Jeringa eVOL® XCHANGE®,
5μL |
|
2910022 |
Jeringa eVOL® XCHANGE®,
50μL, para MEPS |
|
2910028 |
¡Nuevo! Jeringa eVOL® XCHANGE®,
100μL, para MEPS |
|
2910029 |
¡Nuevo! Jeringa eVOL® XCHANGE®,
100μL |
|
2910024 |
Jeringa eVOL® XCHANGE®,
500μL |
|
2910026 |
¡Nuevo! Jeringa eVOL® XCHANGE®,
500μL, para MEPS |
|
2910035 |
¡Nuevo! Jeringa eVOL® XCHANGE®,
1000μL.
NOTA: sólo compatible con eVol® XR |
|
2910030 |
Cargador-Soporte stand
para 1 eVol® |
|
Publicaciones Disponibles |
Resumen |
Ver |
Tamaño |
|
eVol XR - Every One an
Expert |
Ahora con jeringa
XCHANGE de 10 mL |
 |
465 Kb |
|
eVol. Cada Usuario, un
experto |
eVol® son dos
instrumentos de precisión en uno: un motor con control electrónico
digital y una jeringa analítica con adaptador XCHANGE®... |
 |
125 Kb |
|
eVol. Digitally-Controlled
Analytical Syringe |
Existing
liquid handling problems: Pipettors cannot be used for dispensing non-aqueous,
viscous or hazardous liquids. Only positive displacement... |
 |
1076 Kb |
|
Manual eVol. Español |
Gracias por comprar la
Jeringa Analítica Automática eVol®. Ahora tiene la habilidad de
automatizar procesos manuales! Usted irá a disfrutar de la excelencia de
eVol® incorporando nuevas características las cuales no están
disponibles en ningún otro dispositivo de dispensación manual... |
 |
873 Kb |
|
eVol Kit. Detalles de
Producto |
Contents of eVol® Kit (Part
No: 2910000). Initially eVol® will be supplied in a kit which includes
the following components... |
 |
448 Kb |
|
eVol Kit NMR. Detalles de
Producto |
eVol® NMR Edition allows
accurate manipulation of small volumes of NMR samples enabling dilution
directly in the analysis tube – even in tubes with the smallest internal
diameters. eVol® facilitates in-tube sample mixing and enables recovery
of precious samples allowing them to be stored in alternative vessels (such
as inexpensive vials) rather than being left in valuable tubes. These
tubes can now be emptied using eVol®, for washing and re-use. |
 |
318 Kb |
|
eVol Pack Informativo |
eVol® ,
Propuesta de Valor: Para laboratorios que han de dispensar repetidamente
líquidos no
acuosos, eVol® es un instrumento de desplazamiento positivo de control
digital que mejora la
eficacia del laboratorio y mejora la fiabilidad de los resultados. A
diferencia de otros dispensadores
de laboratorio, eVol®
es un dispensador
manual único que puede ser fácilmente calibrado para dispensar líquidos
de manera precisa y exacta independientemente da la habilidad del
usuario. |
 |
260 Kb |
|
Aplicación de Micro-SPE (MEPS) ON-LINE y OFF-LINE
|
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) has revolutionized
sample preparation. Variations on the technique offer enhanced recovery,
greater speciation and reduced solvent and sample consumption over other
techniques. Micro-Extraction Packed Sorbent (MEPS) is the
miniaturization of conventional SPE from milliliter to microliter bed
volumes that allows SPE to be used with very small samples. The
manipulation of the small volumes is achieved with a precision gas tight
syringe. With a typical void volume of 7μL, the MEPS elution is
compatible with GC and LC inlets making it ideal for integration into an
automated sampling system for on-line SPE. |
 |
771 Kb |
|
Preparación de Muestras ON-SITE usando MEPS para
Análisis de Agua Residual |
MEPS uses a barrel insert and needle (BIN) device to
reduce Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) to a micro-scale suitable for small
volume samples and for the on-line adaptation of conventional SPE
techniques. Because the SPE cartridge (BIN) is incorporated into the
needle assembly of a gas-tight syringe, MEPS is also a simple field-portable
SPE device that may be operated manually without need for sampling pumps
or, alternatively, may be incorporated into robotic samplers. |
 |
254 Kb |
|
MEPS para Contaminantes y Muestras de Pequeño Volumen |
MEPS extraction was performed by
diluting 100 μL of a 10-100 ppb standard with 900 μL of water.
• The whole sample was extracted on
a C18 MEPS cartridge conditioned with methanol and water.
• The sorbent was dried and eluted
sequentially with 10 μL of isopropanol and 10 μL of dichloromethane into
the same vial.
• A 1 μL portion of the eluate was
separated on a BPX5 30 m x 0.25 mm i.d. with a 0.25 μm film thickness (SGE
Analytical Science) in a 6890 GC-5973N MSD (Agilent Technologies) fitted
with an ETP 14642 electron multiplier.
• Injection was splitless at a
temperature of 250 °C.
• The carrier gas was helium with a
nominal flowrate of 1.3 mL/min in constant flowrate mode and a nominal
inlet pressure of 10.8 psi. |
 |
506 Kb |
|
Extraction of
Phenols from Waste Water using Micro Extraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS). |
MEPS is the
miniaturization of conventional SPE from milliliter to microliter bed
volumes that allows SPE to be used with very small samples. The
manipulation of the small volumes is achieved with a precision gas tight
syringe.
With a typical void volume of 7 μL, the MEPS elution is
compatible with GC and LC inlets making it ideal for integration into an
automated sampling system for on-line SPE.
To demonstrate the usefulness of MEPS for dilute samples with a
relatively simple matrix, a surrogate wastewater sample was prepared
from clear phenol free waste water spiked with either 25 ppb or 250 ppt
phenols. |
 |
345 Kb |
|
The Micro-Extraction
and Detection of Phenolic Anti-Oxidants from Cereal Products Using MEPS™-GCMS. |
Synthetic
phenolic antioxidants are increasingly rejected as acceptable food
additives because of their demonstrable or suspected adverse effects on
human health. Among the compounds of concern are the butylated
hydroxyphenols such as butylated hydroxy toluene (BHT), butylated
hydroxy anisole (BHA) and bisphenol A. Simple methods for
the removal of
food matrices are necessary for the detection of these compounds in
regulatory compliance programmes. Micro-extraction Packed Sorbent (MEPS™)
is a solid-phase technique that allows rapid sample extraction by
reducing the volume of sample processed. Because the sorbent device is
incorporated directly into a liquid handling syringe, it may also used
with robotic autosamplers for on-line chromatographic analysis. In this
example, rice crackers manufactured with sunflower oil that was
stabilized with BHA |
 |
967Kb |
|
Measuring Fruit
Juice Adulteration by Changes in Flavonoid Content Using MEPS™ and HPLC. |
Cranberry and blueberry
juice are notable example of functional foods that may be eroded in
value by dilution or adulteration with lower value products. The
cranberry is known as a source of polyphenolic antioxidants (including
anthocyanidin flavonoids, cyanidin, peonidin and quercetin) and is the
subject of investigation for potential anti-cancer properties and its
effects on the cardiovascular and immune systems. The tannins are
reputed to reduce urinary tract infections, exhibit anticlotting
properties and reduce gingivitis. Other fruits are also known or reputed
to have functional characteristics and therefore of high value. A rapid
Micro-Extraction Packet Sorbent (MEPS™) method is described for
extracting and concentrating the phenolic components from a variety of
commercial fruit juices. The juice was passed through a C8 or C18 MEPS™
cartridge and the retained fraction eluted with methanol for direct
injection into a HPLC and analysis on a ProteCo™l C18 GP125 column using
a 0.1 % v/v aqueous trifluoroacetic acid – methanol mobile phase.
Detection of the phenolic fraction at 350 nm was used to generate a
characteristic profile for each species of fruit. The method allowed
profiling of fruit juice and the detection of diluents or juice
mixtures. Because the solid-phase step is flowrate dependant, the small
sample and elution volumes of MEPS™ allow rapid sample extraction that
may be completed in realtime with the HPLC analysis. |
 |
701Kb |
|
Aplicación de MEPS acoplado a GC-TOF MS en el
Análisis de Retardantes de Llama Bromados en Agua Residual |
In last years, miniaturized
analytical techniques had gained attention due to its many special
features over classical approaches. Among many advantages, usage of
little or no solvent,
increasing of sensitivity of analysis and user-friendly system, should
be pointed out. Micro
extraction in packed sorbent (MEPS) is a new technique for miniaturized
solid-phase extraction that
can be connected online to gas chromatography (GC) or liquid
chromatography (LC) without other sample pre-treatment.1-4 The sample
(10–250 μL) is withdrawn through the syringe by an autosampler. When the
sample has passed through the solid support, the analytes are adsorbed
to
the solid phase packed in a barrel insert and needle (BIN). The solid
phase is washed afterwards by water to remove any interfering material,
and the elution of analytes is performed directly into the instrument’s
injector by organic solvent (in case of GC), or the LC mobile phase. The
large injected volume, typically from 10 to 50 μL, may imply the use of
programmed temperature vaporiser (PTV) and large volume injection (LVI).
Moreover, a large variety of special packed materials in BIN, such
restricted access material (RAM) or molecular imprinted polymers (MIPs),
can be used. |
 |
283 Kb |
|
The Extraction and Analysis of Urinary Antitussive
Metabolites using MEPS™ and ESI-LCMSn |
Microextraction Packed Sorbent
(MEPS™) is an adaptation of SPE into a miniaturized device with a
typical void volume of less than 10 μL. With operating volumes of this
scale and its compatibility with autosampler syringes, MEPS™ allows the
specificity of the solid-phase process to be harnessed for digital
chromatography using discontinuous changes in solvent polarity. The
eluant volumes are sufficiently small to be injected directly into a
HPLC system and therefore permit the on-line use of solid-phase
extraction methodology in real time with the HPLC. |
 |
122 Kb |
|
MEPS: A New Technique for the
Analyisis of Small Brominated and Chlorinated Aromatic Compounds in Wine |
The wine industry has long
suffered from TCA (2,4,6-trichloroanisole) and TBA (2,4,6
tribromoanisole) contamination or “cork” taint. These compounds more
recently has been found to be present in corks, packaging material,
cardboard boxes, wooden products and many other materials. Only 1-2 ng/l
of TCA or TBA is required to give wine the “musty” aroma associated with
cork taint. It has been proposed that chlorophenols are the precursor
for TCA (Fig1). As dioxins are known to be present as contaminants in
chlorophenol formulations (1) they might therefore also be present in
the wine corks, a hypothesis that needs further invesitigation. In this
work, the analysis of TCA and TBA is performed by a new technique for
sample preparation called Microextraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS). This
technique in combination with different GCMS techniques is described
below and compared with other methods. |
 |
318 Kb |
|
The application of MEPS for the
on-site preparation of water samples |
MEPS uses a barrel insert and
needle (BIN) device to reduce Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) to a micro-scale
suitable for small volume samples and for the on-line adaptation of
conventional SPE techniques. Because the SPE cartridge (BIN) is
incorporated into the needle assembly of a gas-tight syringe, MEPS is
also a simple field-portable SPE device that may be operated manually
without need for sampling pumps or, alternatively, may be incorporated
into robotic samplers.
To demonstrate the application of MEPS we report the qualitative field
use of C18-MEPS for the sampling of water bodies in both industrial and
urban environments. Water samples were extracted on-site and then the
MEPS
syringes were transported back to the laboratory overnight for elution
and analysis of the retained components.
C18-MEPS was used to extract samples (100-1000 μL) of water from
industrial drains and stormwater pipes to recover semi-volatile residues
for GCMS analysis (Fig 1-3). The technique was also applied to sampling
droplets on surface extracts of paint for non-destructive surface
profiling (Fig 2). Analysis of the unknown samples was qualitative but
sufficiently sensitive to detect industrial discharge residues
associated with grinding coolants, packaging materials and other
contaminants. Naturally occurring leachates from vegetation were also
detectable. Droplet extraction of a painted surface was performed in
reversed-phase mode (water extract on C18 sorbent) and allowed the
surface to be profiled for comparative purposes. |
 |
926 Kb |
|
The Integration of
Microextraction Packed Sorbent (MEPS) into Multidimensional Strategies |
LC-GC approaches to analysis
are particularly attractive because they combine the selectivity of
solidphase
sorbents in the first dimension with the separating power and peak
capacity of a capillary GC column in the second and subsequent
dimensions. Widespread use of the technique is limited because of the
difficultly in desolvating
the stream from the LC dimension without the solvent vapour passing down
the GC column in significant quantity.
An alternative approach to elution chromatography in the first dimension
is to harness the specificity of the solid-phase process for digital
chromatography using discontinuous changes in solvent polarity (Fig 1).
Digital chromatography on a small sorbent bed reduces the volume of
mobile phase to discrete plugs that are sufficiently small to be
injected directly into a GC with a large volume injector or,
alternatively, subsampled into a conventional split/splitless injector.
Microextraction Packed Sorbent (MEPS) is an adaptation of SPE that
incorporates all the desirable characteristics
into a miniaturized device with a typical void volume of less than 10 μL.
With operating volumes of this scale and its compatibility with
autosampler syringes, the MEPS format is the ideal for a digital LC -
elution GC approach to analysis.
In this application, we use the selectivity of an argentation sorbent to
speciate a mixture of fatty acid methyl
esters on the basis of unsaturation in the first dimension and then to
separate groups by conventional non-polar GCMS in the second dimension. |
 |
724 Kb |
|
Argentation Based (MEPS) for
the Analysis of FAMES by GCMS |
Micro Extraction by Packed
Sorbent (MEPS) is an adaptation of SPE that incorporates all the
desirable characteristics into a miniaturized device with a typical void
volume of less than 10 μL. With operating volumes of this scale and its
compatibility with autosampler syringes, MEPS allows the specificity of
the solid-phase process to be harnessed for digital chromatography using
discontinuous changes in solvent polarity (Fig 1). The eluant volumes
are sufficiently small to be injected directly into a GC with a large
volume injector or, alternatively, subsampled into a conventional split/splitless
injector and therefore MEPS can be used as a digital LC - elution GC
approach to analysis.
In this application, we use the selectivity of an argentation sorbent to
speciate a mixture of fatty acid methyl
esters on the basis of unsaturation in the first dimension and then to
separate groups by conventional non-polar GCMS in the second dimension. |
 |
626 Kb |
|
Microextraction Packed Sorbent
(MEPS): Analysis of Food and Beverages |
MEPS is a development of
conventional SPE that has miniaturised the sorbent bed so that it can be
incorporated into the sample path without voids. Typically, a MEPS
method reduces sample and reagent consumption by several orders of
magnitude over conventional methods. Extraction performance is
comparable to conventional SPE because the MEPS sorbent bed retains the
same dimensional ratios of the conventional device and adaption of
existing methods is achieved by scaling all steps in proportion to the
bed volumes (typically 1 mL for SPE and 10 μL for MEPS). The small scale
of the MEPS device allows elution in a small volume and so the entire
extract may be analyzed rather than only using a portion of the prepared
extract in a conventional experimental design. SPE and MEPS are not the
same as SPME or SBSE techniques. The former rely on solvent desorption
and use a mono-layer extraction surface with a very large surface area.
The latter are immobilised liquid extraction techniques that are
typically used in thermal desorption mode. |
 |
484 Kb |
|
The Extraction of Saliva
for The Analysis of Basic Drugs Residues Using MEPS™-GCMS. |
Oral fluid is considered a
desirable sample for regulatory screening of drugs of abuse and for
clinical monitoring because it may be collected in a non-invasive
fashion when compared with the procedures used for collection of
urine and blood. Unlike urine, the appearance of the drug residues
in saliva may be directly correlated with plasma drug concentrations.
The relatively low concentration of most drugs in saliva and the
small sample volume that is typically available for analysis makes
micro-extractive techniques both attractive and necessary for this
matrix. MEPS™ is a micro-scaled SPE device that is incorporated
directly into a liquid handling syringe and may be used
with robotic
autosamplers for on-line chromatographic analysis. The small scale
of the MEPS™ device is effective
for the extraction of small volume
samples and is therefore potentially valuable for the extraction of
oral fluids for GC-MS confirmatory analysis. We present here a
simple reversed-phase C18-MEPS™ extraction for saliva collected from
a patient that had been administered the local anaesthetic
mepivacaine for a dental procedure several hours previously. |
 |
206 Kb |
|
The Determination
of Urinary Metabolites of Dextromethorphan by Meps™-Esi-Lcms. |
Micro Extraction by Packed
Sorbent (MEPS™) is an adaptation of SPE into a miniaturized device with
a typical void volume of less than 10 μL. With operating volumes of this
scale and its compatibility with autosampler
syringes, MEPS™
allows the specificity of the solid-phase process to be harnessed for
digital chromatography using discontinuous changes in solvent polarity.
The eluant volumes are sufficiently small to be injected directly into a
HPLC system and therefore permit the use of solid-phase extraction
methodology in real time with the HPLC.
In this application, we describe the analysis of naturally voided human
urine samples that were collected following the administration of single
doses of dextromethorphan for both the parent drug and its urinary
metabolites. The effectiveness of MEPS™ is compared with the same sample
prepared off-line using conventional cartridge SPE. The method was used
to demonstrate the effectiveness of MEPS™ for extraction
of biological fluids for LCMS
analysis. |
 |
792 Kb |